What is a data diode?
A data diode is a cybersecurity solution that ensures unidirectional information exchange. Learn more why you need it and how it communicates with bidirectional protocols.
How does a data diode work?
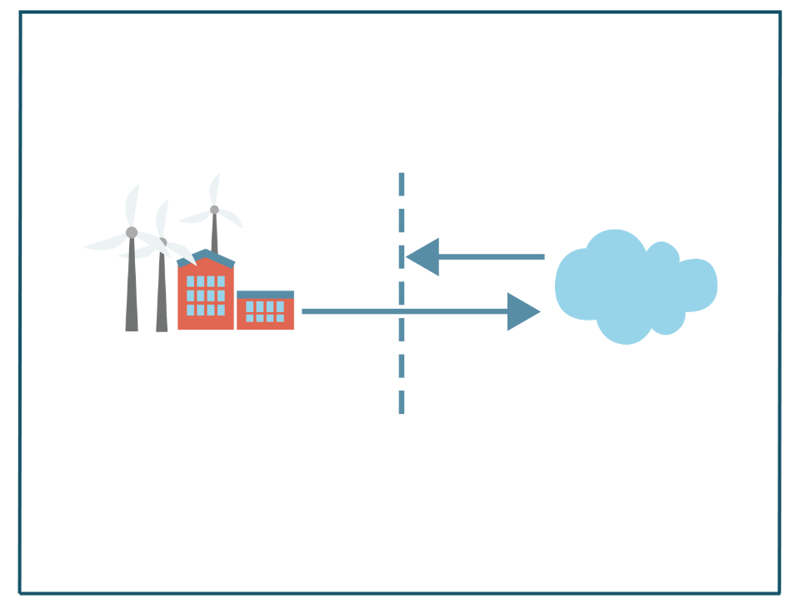
Data diodes are the fail-safe way to protect sensitive systems and confidential data. A data diode is a security product that is placed between two networks and acts as a non-return valve whose function only allows data to be sent in one direction while blocking all data in the opposite direction.
Since the security properties of the data diode are based on hardware and optical fiber, it can be shown that it is physically impossible for data to be transported in the opposite direction. Because security is not based on software, there are no vulnerabilities in the form of software bugs, nor can it be attacked by malicious code. Hardware-based security means that you can show that data diodes have high assurance.

Why do you need a data diode?
A common solution to keep sensitive or classified information safe from leakage or manipulation is to completely disconnect it from other networks. However, there are situations when data needs to be transferred to or from the protected network.
The most common device used for regulating information flow is probably a firewall. This is a device with the purpose to protect your network by only allowing certain traffic to enter it. It monitors and filters what traffic and data-packets that enter the network, and which are blocked based on a set of rules. However, if you need to transfer information to or from a security sensitive network a firewall is not the only product in your toolbox to enhance your cybersecurity.
Though a firewall strives to protect the network, a high assurance addition in terms of a Cross Domain Solution is also needed. Cross Domain Solution (CDS) is a term used to describe the concept of maintaining secure information exchange between domains with different security or protection needs. This can be between databases, servers, applications, or combinations of these. CDS addresses the concept of communicating, sharing or moving information between domains and applies validation, transformation or filtering to the exchange. The data diode is a Cross Domain Solution.
By using a data diode, you can ensure that the transfer is done securely without jeopardising the integrity or the confidentiality of the network.
Who needs a data diode?
A high assurance data diode protects assets for operators within critical infrastructure (ICS/SCADA) and defense industries. However, along with digitalisation and the increase of sophisticated cyberattacks, every organisation that operates with sensitive information has great use of a data diode to protect its valuable information and securely exchange data.
Regulations where a data diode can help you comply
If you are affected by the NIS Directive, DORA or the new EU rules on cybersecurity aspects of cross-border electricity flows, you can benefit by using data diodes in your security solution.
The NIS Directive
Network segmentation in data networks means dividing a data network into subnetworks, where each is a network segment and is mentioned in one of the reasons for NIS 2 (preamble 89) as a necessary and basic cyber hygiene factor, and again (preamble 98) to secure electronic communication services and networks. Using data diodes for your network segmentation maintains both the integrity of the network by preventing intrusion and the confidentiality of the network by protecting the most sensitive information.
You place the data diode between two networks and it then acts as a check valve whose function only allows data to be sent in one direction while blocking all data in the opposite direction. Since the security is not based on software, there are no vulnerabilities in the form of software bugs, nor can it be attacked by malicious code. Hardware-based security means that you can be sure that correctly designed data diodes meet their security requirements with a high degree of assurance.
Read more about network segmentation.
DORA
Also DORA refers to network segmentation. According to Article 9 of DORA, financial actors must design the infrastructure for network connection in a way that allows it to be immediately separated or segmented in order to minimise and prevent proliferation, especially for interconnected financial processes – i.e. you need to work with network segmentation and using data diodes in your security solution will give you a secure solution.
DORA also refers to secure updates – another area where data diodes can be of use. According to Article 16 of DORA, the relevant organisations shall minimise the effects of ICT risk through the use of sound, resilient and up-to-date ICT systems, ICT protocols and ICT tools suitable to support the performance of operations and the provision of services and on a adequately protect the confidentiality, availability, integrity or authenticity of the data in the network and information systems.
Updated systems are an important part of being able to maintain the security of the digital information contained in the systems. However, the update may involve a security risk and to avoid that and to maintain the integrity and availability of the systems and to be able to make secure updates, special solutions are required. One way to do a secure update is to use a data diode that ensures one-way communication. The data diode is connected so that information can be imported into the system, but since no traffic can be transmitted in the opposite direction, information leakage is made impossible.
Read more about secure updates.
New EU rules for electricty flows
On 13 June 2024, new EU rules on cybersecurity aspects of cross-border electricity flows came into force. The new regulation should contribute to strengthening the electricity system’s resilience against cyberattacks.
To strengthen your cyber resilience, there are several things you can do. Two of these important things are:
Make sure all software is up to date
Use appropriate network segmentation
Data diodes can be your security solution for both of these, as mentioned regarding the NIS Directive and DORA.
Five things you can use data diodes for
If a data diode is directed out from the high security network towards a network with a lower security level, data can be transferred from the high security network while the high security network stays protected. By transferring information via a data diode, you are guaranteed that no one can use the same connection in the opposite direction to reach the high security network and disrupt the availability and integrity of the systems.
A data diode can also be directed towards the high security network. In these cases, it is most likely that you want to collect information of some kind from another network. The security issue, however, is how to collect the information and at the same time make sure that there is no leakage of sensitive data from your network through this channel. A data diode will ensure the confidentiality of the high security network by preventing any form of data leakage from happening.
There are more ways to use a data diode than you might think. You can use them for countless solutions, but here are five areas you may not have known about in which you can use data diodes:
IoT sensor networks
HTTP mirror
Traffic tapping
Video streaming
Logging
You can read more about how you can use data diodes in these five areas here.

Other solutions for segmentation
Bidirectional security gateways
A Security Gateway can be compared to a firewall as it regulates what traffic that can enter and exit a network. A Security Gateway only forwards received information when it complies with a certain policy which is derived from your organisation’s information security policy. The policy implemented in the Security Gateway defines accepted structures, formats, types, values, and even digital signatures. When a message is sent from one security domain to another across the Security Gateway, information in the message is analysed and validated according to the configured policy. Approved parts of the received message are put into a new message which is sent to the intended receiver in the other domain. In this way, you know that only allowlisted information crosses this boundary.
Air gap
Air gap means that a computer or a computer network does not have connections to the outside world. Physical security such as locks, guards and alarms prevent unauthorised access, as well as logical access control once you are at the computer. Information is moved in and out of the environment via portable media. The information must be checked before it is imported so that it does not contain malicious code, but also during export so that you do not accidentally export “wrong” information and thus risk revealing it. Air gap is thus a relatively manual system used to protect sensitive information and sensitive environments.
Strengths with a data diode
There are several strengths with a data diode:
Their ability to ensure security in insecure systems, and to protect and preserve legacy systems. By using data diodes, legacy systems can be protected without overhauling the entire operational system.
Its hardware aspect. By using a hardware system, data diodes remove, to a large extent, the possibility of user error.
The long-term operating costs are low. After initial investment of purchase and system integration, the savings in maintenance and administration costs make the data diode an efficient network security solution in the long run.
The way they reduce the cybersecurity risk. The diode’s strict properties mean that you can completely rule out certain types of risks if you use a diode. For example. you know that the network can not leak information and can thus only focus on managing risks with privacy and malware.
Read more about Advenica’s data diodes.
Use Cases where data diodes can be used
Here some different use cases where data diodes can be used to increase security:
import and export files between different zones
connect a integrity-sensitive OT system to other systems
centralised log collection in security-sensitive systems
transfer critical information, eg from a SCADA system to an administrative office network
Windows and Linux system updates
Read more about the different Use Cases.
Benefits with Advenica’s data diodes
There are many benefits with using data diodes – below, we have listed 14 of the benefits that Advenica’s data diodes have.
1. Meets the highest security requirements
Advenica’s data diodes meet the highest demands on both security and assurance. Internal separation of functions, multi-stage unidirectional security and deep security analysis provides trust and high assurance. Special attention has been given to eliminate the risk of covert channels in the reverse direction. Advenica’s data diodes DD1000A and DD1000i are also approved by the Swedish Armed Forces with component assurance level N3, according to Swedish national security requirements. Component assurance level N3 can be used in systems with high impact level (e.g. handling secret information up to SECRET/TOP SECRET) but where the component level of exposure is somewhat limited.
2. Different data diodes for different purposes
Advenica’s portfolio consists of data diodes of different types, ranging from small DIN mounted devices to 19” rack mounted devices. You can choose from having proxy computers integrated in the diode chassis or purchasing a simpler data diode device and deploying the proxy software in external proxy machines.
3. Made in Sweden
Advenica’s data diodes are designed, developed and manufactured in Sweden. By controlling every step from design to aftermarket, we can ensure confidence in our security features. This enables us to develop high-security products for critical data up to Top Secret classification.
4. Possibilities for customer alterations
Does the list of supported protocols not satisfy your needs? Tell us about your use case and let our Customer Solutions team develop specific features based on your needs. Everything from feature growth in the platform itself to support for additional protocols is possible.
5. Easy to administrate
Data diodes are easy to install and configure, and a simple standard use case can be deployed in a couple of hours. Monitoring is done using standard methods such as SNMP and Syslog that allows integration with all widely used network monitoring tools. Configuration changes are applied using a simple to use web application interface.
6. Defence-in-depth
Advenica’s DD1000i data diode is designed according to the principle of defence-in-depth where the proxies and the data diode act as different layers of security controls. The proxies block all communication not explicitly allowed and the data diode module blocks, with very high assurance, all information transfers in the forbidden, reverse direction.
7. No dead code
Advenica’s DD1000i contains no dead code. Configure and upload a custom configuration to the device based on the specific protocol support you need. There is no way to activate or change the supported protocols without uploading a new configuration to the device. Hardened OS – only the necessary packages to support normal operation are included in the firmware running on the device.
8. Unique certification – N3
Advenica’s data diodes have a unique certification for N3 in Sweden – we are the only ones with this certification level in Sweden. N3 is a certification issued by the Swedish Armed Forces. Data diode DD1000A and data diode DD1000i are approved by the Swedish Armed Forces with component assurance level N3, which e.g. handles data up to, and including, level HEMLIG/ SECRET, according to the Swedish Armed Forces’ Requirements for Security Functions (KSF).
Read more about our certifications.
9. Full galvanic separation
Data diodes DD1000A och DD1000i: Special attention has been given to eliminate the risk of covert channels in the reverse direction, resulting in functions like one PSU for each side of the data diode, and RFI/ EMI-reducing internal enclosures to minimise compromising emanations.
10. Separation of duties
Separation of duties is supported, different interfaces for data transfer and admin/log data.
11. Higher assurance
Data diodes offer an extremely high assurance level. You can actually say that a data diode corresponds to an air gap in the reverse direction. We have shown to an external evaluator that there are no currently known physical phenomenas that can be used to transmit information in the reverse direction.
Read more about how data diodes can be considered as an effective alternative to air gaps.
12. Redundant power supply
To ensure high availability, data diode DD1G supports redundant power supply. In our other data diodes, for assurance reasons, there is no electrical connection between the two sides, which makes redundant power supply difficult.
13. Minimise the risk of lost data
Data diode DD1000i has specially adapted software to minimise the risk of lost data between the sending and receiving proxy.
14. Products that live long
Data diodes DD1000A and DD1G are constructed with components that have a very long life and lack mechanically moving parts such as fans or processors. Once you have installed these data diodes, you do not need to do any updates. The MTBF for these products is 91,000 hours, i.e. just over 10 years.
This is how you motivate adding a data diode to your budget
Investing in a data diode means investing in a high-security solution – it cannot be compared with ordinary measures for IT security. If you need to transfer information to or from a security-sensitive network, “regular” IT security is not the only solution you should choose.
Sometimes you may need to justify why you need to make a certain investment. To make it as easy as possible for you, we have listed several arguments that you can use to motivate an investment in a data diode!
The alternative cost can become very high
Present a calculation of how much money the investment can save you
A data diode means lower OPEX costs
Want to invest in your cybersecurity? Contact us today.








