What is cybersecurity?

What is cybersecurity and why is it so important? How do I start working with information security? Reduce the risk of cyberattacks by learning how to become cybersecure!
Lack of cybersecurity is a major risk to businesses today. We read all the time about companies that have been attacked, with a great cost to both the business and the customers. Cybersecurity really is a buzzword in this digital world. But what is the definition of this word? And why do I need to bother about cybersecurity and cyberattacks? Read on and learn how to work with cybersecurity and thus can protect your critical information.
The definition of cybersecurity
There are several definitions of the word cybersecurity but they all have in common that cybersecurity is comprised of an evolving set of tools, risk management approaches, technologies, training, and best practices designed to protect networks, devices, programs, and data from attacks or unauthorised access.
Cybersecurity is the practice of defending computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks
Cybersecurity vs information security
Is there really a difference between cybersecurity and information security? One of the main reasons for these two terms to be used interchangeably is that both cybersecurity and information security are related to security and safekeeping a computer system against data threats and information breaches.
But while cybersecurity is about protecting networks, devices, programs, and data from attacks or unauthorised access, information security is above all about preventing information from being leaked, distorted, and destroyed. Information security is also about all data, no matter its form. This means that in information security, the primary concern is protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. In cybersecurity, the primary concern is protecting against unauthorised electronic access to the data.
Read more about information security.
Why is cybersecurity important?
The world relies on technology more than ever before. Businesses and governments store a great deal of data on computers and transmit it across networks to other computers. More and more systems are connected, and as the digitalisation continues this will certainly continue as well.
The digitalisation is not only positive, it also means that we get more vulnerable. Devices and their underlying systems have vulnerabilities that, when exploited, undermine the health and objectives of an organization. And the problem is that the vulnerabilities are being used for cyber-attacks.
Cybersecurity can be used to counteract three types of threats: cybercrime, where single people or groups attack systems for financial gain, cyber warfare, often related to information gathering and politically motivated, and cyber-terrorism, which is intended to undermine electronic systems and cause panic or fear.
Cyber hygiene – what is that?
Maybe you have also heard about cyber hygiene? Cyber hygiene is a subset of cybersecurity—it’s about the routine, everyday practices that individuals and organisations should follow to maintain security and reduce risks. Think of it like personal hygiene: brushing your teeth doesn’t replace going to the dentist, but it helps prevent problems.
Cyber hygiene is essential for maintaining strong cybersecurity and here are some essential cyber hygiene practices:
Strong passwords: Use complex passwords and a password manager.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA for extra security.
Software updates: Regularly update operating systems, apps, and antivirus software.
Phishing awareness: Recognise and avoid phishing emails and scams.
Secure Wi-Fi & VPN Use: Encrypt connections, avoid public Wi-Fi, and use a VPN.
Data backup: Regularly back up important files to an external drive or cloud storage.
Device security: Lock screens, use biometric authentication, and disable unused Bluetooth connections.
Some common cyber hygiene mistakes are to reuse passwords across multiple accounts, to click on suspicious links or attachments or to ignore software updates or forget to verify sources before sharing personal information.
All of these mistakes can lead to serious security problems.
The increasing cyber threat
A more digitalised world means more and more opportunities for attackers to strike. For example, the use of connected “smart” products, also called IoT devices, is increasing rapidly. The more products that are connected to your network, the more ways in exist for a potential attacker.
It has become apparent recently that thinking about security yourself is no guarantee – if your suppliers do not do it. An attack against your supplier can affect you to a very large extent, depending on the part the supplier has in your business.
It has also become more common with cyberattacks with higher aims than making money – attacks on critical infrastructure and national databases are today a fact and are something that can ultimately cost society money, sensitive information, and lives. Despite this, there is currently not enough competence in the cybersecurity area.
Different types of cyber threats
There are several different types of possible cyber threats:
Malware
Malicious software such as computer viruses, spyware, Trojan horses, and keyloggers.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a form of malware that locks or encrypts data until a ransom is paid which may or may not give the victim access to the files again.
Phishing Attacks
The dishonest presentation of e.g. an e-mail or fake website that enables someone to retrieve sensitive information from the person that has received the message/visited the link (for example passwords or credit card information).
Social engineering
The psychological manipulation of individuals to obtain confidential information – this often overlaps with phishing.
Cyberattacks can have serious consequences
Being exposed to a cyberattack can have serious consequences for the affected company/organisation:
Large productivity losses as the attack can lead to interruptions and even longer production stops. The attack can also result in a more lasting deterioration in productivity.
Leakage or even loss of personal information about customers. Intellectual property rights are also at risk of being stolen.
The trust and reputation of the company can be severely damaged, which can lead to difficulties in gaining new customers in the future and difficulties in obtaining financing.
Large costs can arise in connection to the attack, among other things to pay external service providers to solve the problems with shut down computers and more, but also for extra work internally to solve the situation. It can also entail costs if you as a company do not meet the various requirements placed on the business.
There is a risk that the company will be forced to close its entire business, at least temporarily, which for a lot of businesses that are based on the fact that they are constantly running is a serious threat.

Who needs cybersecurity?
The simplest and perhaps obvious answer is that all organisations have sensitive data that is vulnerable to cyber attacks. That is why it is critical for everyone to employ steps to improve their posture and reduce their risk.
Some critical sectors are in the limelight more frequently when it comes to cybersecurity, and for good reason:
Government and Critical Infrastructure
Cybersecurity is crucial for governments and other organisations that directly affect the nation’s – or world’s – wellbeing and safety. Critical Infrastructure have many national security and safety implications. Cyberattacks to critical infrastructure sectors can be catastrophic, causing physical harm or severe disruption in services.
Companies under compliance and regulations
Many organisations operate under government or industry regulations that include a cybersecurity component. These standards ensure that companies take precautions to protect consumers’ data, and even sensitive government and military data, from cybersecurity threats.
Business to Business (B2B)
If your business is considered a small to medium enterprise, you may have larger clients starting to perform third party risk assessments on their vendors (which includes you). This means they start requiring that all their vendors meet certain levels of cybersecurity. This is becoming best practice as larger organisations are working hard to protect themselves, knowing smaller organisations are at risk and can serve as the conduit for attackers into the larger organisations.
Regulations that require companies to work with cybersecurity
During the recent years many new regulations, like the NIS Directive and stricter national security legislation have been implemented.
The NIS Directive aims to promote security measures and boost EU member states’ level of protection of critical infrastructure. In other words, it improves information security of operators in sectors that provide essential services to our society and economy.
The Swedish Protective Security Act clarifies the obligations for companies with security-sensitive activities and the importance of the operators performing security protection analyses for their operations.
In 2020 the new EU guidelines regarding cybersecurity for banks came into force. Now it is clearer how various financial services are to manage internal and external risks linked to IT and security.
And there is now also a proposal for mandatory adjustments in Livsmedelsverket’s regulations on information security for socially important services. This proposal primarily concerns municipal administrations, companies and administrations that own a public water supply system and thus provide public drinking water.

Benefits of cybersecurity
The benefits of utilising cybersecurity are obvious, and include things like:
Protect networks and data from unauthorized access
Improved information security and business continuity management
Improved stakeholder confidence in your information security arrangements
Improved company credentials with the correct security controls in place
Faster recovery times in the event of a breach
How to start working with cybersecurity?
To start with every business or organisation must identify which information that is most critical and thus worth protecting. As most systems today are interconnected it is difficult to have an overview of how many paths that lead to the most valuable information. By using a risk and security assessment, all loopholes can be detected.
However, it is neither practical nor economically justifiable to protect all information in the same way. To secure the most valuable information, strict network segmentation is the best solution to use. This means you create zones with different security levels.
When you have created your zones you should choose security solutions for operation, accessibility and adaptability based on the attacker's perspective and the worst-case scenario. To be able to protect your most critical information, make sure to use professional high assurance solutions that are future-proof.
![]()
Cybersecurity checklist - 8 pieces of advice when starting with information security work
It is not always easy to know where to begin. Here are eight pieces of advice to get you on the right track.
Realise that information security means more than technology
Information security work has to be linked to your organisation's risk management
Ensure that management takes its responsibility
Review procedures and processes
Ensure that the right resources are available
Start with a security analysis that identifies assets and threats
Develop a security policy (this helps you to maintain information security)
Get help from those with in-depth information security knowledge
Read more about these steps in our guide.
Want some more advice on how to invest in your cybersecurity? Contact us today.
Different types of cybersecurity products
There are a number of products that can strengthen your cybersecurity, but here are a few.
VPN encryptors
Sometimes, it is necessary to communicate over the Internet, but the sensitivity of the information can hinder you from being able to openly send it to the recipient. The solution is to use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) encryptor. VPN encryptors can be used to protect your network, while connected to the Internet, by creating secure and private tunnels between a device and a network, or between two networks. In this way, you can be connected to the Internet, but the information you send to other units within the private network is encrypted and securely sent through the tunnels, resulting in traffic that cannot be read by anyone outside of your private network. You are thereby protecting your network by protecting how the information flows between units or networks.
Many encryption solutions are mainly software-based, like the solutions used for remote work. These solutions are simple to use and not so expensive but are not made for information at the highest security level. Purely software-based solutions are simply not enough for providing top-level security due to vulnerabilities to advanced attacks, but they can be enough for other use cases.
Hardware-based encryption solutions are more expensive and can be a bit more complicated to handle, but if you have sensitive information or information that needs stronger protection – which makes security the highest priority – hardware solutions should be your choice.
Read more about Advenicas solution SecuriVPN.
Firewalls
A firewall protects your network by only allowing certain traffic to enter or exit. It monitors and filters traffic based on rule setups.
With a firewall, it is difficult to know exactly what information is being exported or imported into the system. A firewall configuration often becomes complex, which increases the risk of misconfiguration. Firewalls also do not separate administration and data flow in a way that protects the information from insiders. Organisations that have sensitive information and that operate in critical infrastructure, public sector or the defence industry, need their networks to keep a higher level of security. That is why more solutions than a firewall are often needed.
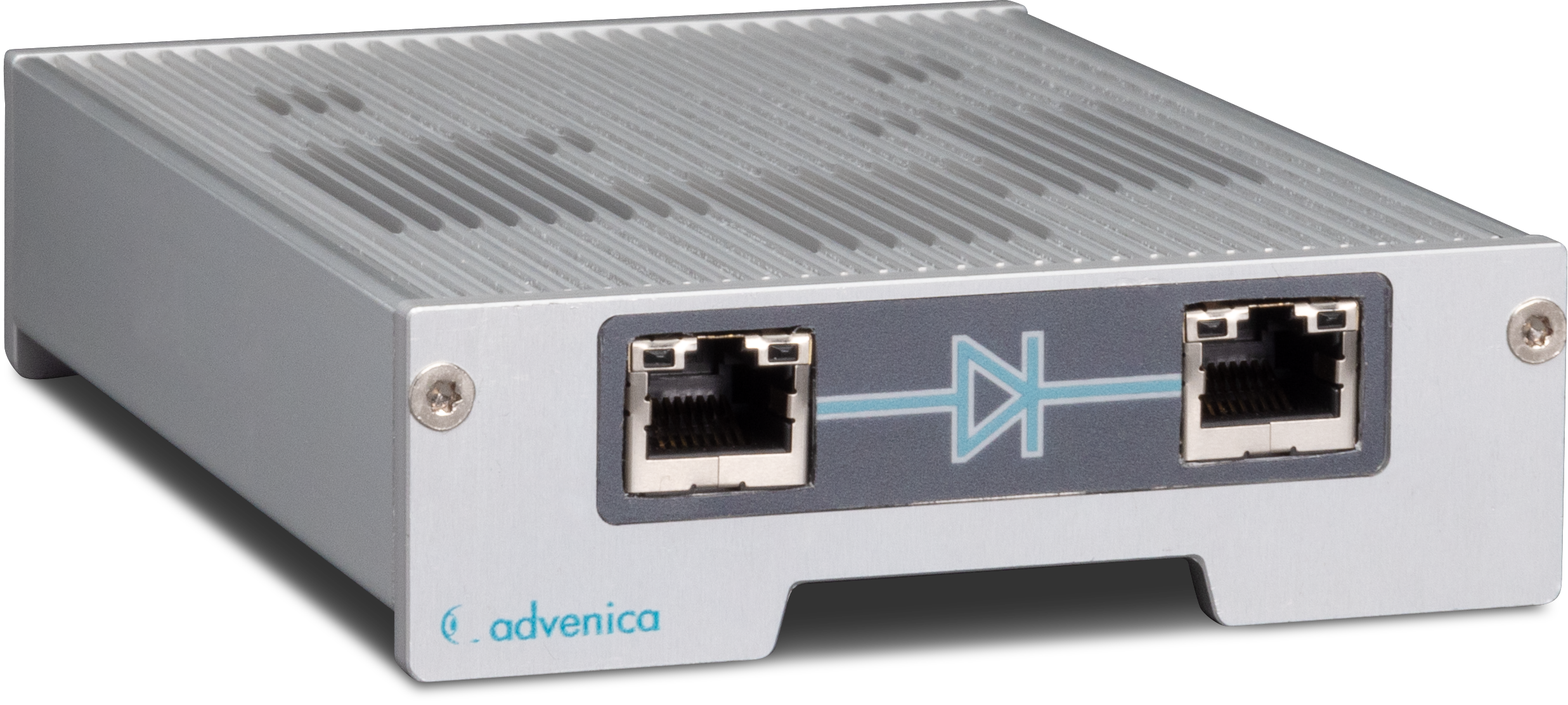
Data diodes
A data diode is a cybersecurity solution that ensures unidirectional information exchange. This high assurance hardware device maintains both network integrity by preventing intrusion, as well as network confidentiality by protecting the most security sensitive information.
Data diodes are the failsafe way to protect sensitive systems and confidential data. Data diodes are small hardware devices, also called “unidirectional security gateways”, which sit between two networks. Working like a check valve, the function of a data diode is to allow all data to pass in the forward direction, while blocking all data in the reverse direction. And as it is not software, it cannot be directly attacked by malicious code, which results in high assurance.
Read more about data diodes and how they work.
Security Gateways
A security gateway is a device that controls the information exchange that takes place between different security domains.
If you have security sensitive or even classified information, you may need a solution that offers secure and filtered bidirectional communication. In this case, you need to ensure secure bidirectional communication and be sure that nothing malicious enters your sensitive networks, and that sensitive information and data does not leak to a less sensitive and less protected network.
The purpose is to apply strict information-level control during information transfers and mitigate cybersecurity threats such as manipulation, data leakage and intrusion. A security gateway only forwards received information when it complies with its policy which is derived from your organisation’s information security policy. The policy implemented in the security gateway defines accepted structures, formats, types, values and even digital signatures. When a message is sent from one security domain to another across a security gateway, information in the message is analysed according to the configured policy. Approved parts of the received message are put into a new message which is sent to the intended receiver in the other domain. In this way, you know that only allowed information crosses this boundary.
Advenica’s solution is ZoneGuard, read more about it.
We have the cybersecurity solutions you need
What are your security challenges?
Do you need to securely integrate IT and OT systems?
Do you need to secure your remote access?
Do you want to be able to transfer sensitive information from a SCADA system?
Do you have to find a secure solution for traceability and logging?
Want to avoid the security risks with updating your systems?
Do you need secure communications with remote sites?
Read more about how our use cases can help you with these and similar challenges.