We believe that secure information flows are necessary for you to be respected as an attractive employer and leading-edge business. Responsible information management gives you the ability to achieve viable and sustainable businesses that open up for innovation and new revenue opportunities.

Information management as part of CSR
Companies need to change the way they view sustainability, and weave information management into the more traditional parameters of CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) efforts such as environment, working conditions, effects on society etc.
Information today is a giant building block for almost every part of society. And some of this information should and must be protected.
Information security should become a topic discussed and prioritised more often in boardrooms and management. This is vital as taking digital responsibility can be very important for effects on society. Protecting information and using/building secure systems should be a clear part of CSR, or CDR (Corporate Digital Responsibility), that every company should follow as this becomes more and more important, not only for the companies themselves, but for the security of our society.
Future proof solutions help you take your digital responsibility
Future proof solutions for information security – that is what you need to be able to take your full digital responsibility. This means you have to ensure that your supplier has a working method that means that they will continue to be digitally responsible. Do they provide security updates throughout the product life cycle? Is their product/solution future proof? These are important questions you need to ask your supplier of information security solutions.
Different types of cybersecurity products for your digital responsibility
There are a number of products that can strengthen your cybersecurity, but here are some of them!
VPN encryptors
Sometimes, it is necessary to communicate over the Internet, but the sensitivity of the information can hinder you from being able to openly send it to the recipient. The solution is to use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) encryptor. VPN encryptors can be used to protect your network, while connected to the Internet, by creating secure and private tunnels between a device and a network, or between two networks. In this way, you can be connected to the Internet, but the information you send to other units within the private network is encrypted and securely sent through the tunnels, resulting in traffic that cannot be read by anyone outside of your private network. You are thereby protecting your network by protecting how the information flows between units or networks.
Many encryption solutions are mainly software-based, like the solutions used for remote work. These solutions are simple to use and not so expensive but are not made for information at the highest security level. Purely software-based solutions are simply not enough for providing top-level security due to vulnerabilities to advanced attacks, but they can be enough for other use cases.
Hardware-based encryption solutions are more expensive and can be a bit more complicated to handle, but if you have sensitive information or information that needs stronger protection – which makes security the highest priority – hardware solutions should be your choice.
Read more about encryption and the Advenica solution SecuriVPN!
Firewalls
A firewall protects your network by only allowing certain traffic to enter or exit. It monitors and filters traffic based on rule setups.
With a firewall, it is difficult to know exactly what information is being exported or imported into the system. A firewall configuration often becomes complex, which increases the risk of misconfiguration. Firewalls also do not separate administration and data flow in a way that protects the information from insiders. Organisations that have sensitive information and that operate in critical infrastructure, public sector or the defence industry, need their networks to keep a higher level of security. That is why more solutions than a firewall are often needed.

Data diodes
A data diode is a cybersecurity solution that ensures unidirectional information exchange. This high assurance hardware device maintains both network integrity by preventing intrusion, as well as network confidentiality by protecting the most security sensitive information.
Data diodes are the failsafe way to protect sensitive systems and confidential data. Data diodes are small hardware devices, also called “unidirectional security gateways”, which sit between two networks. Working like a check valve, the function of a data diode is to allow all data to pass in the forward direction, while blocking all data in the reverse direction. And as it is not software, it cannot be directly attacked by malicious code, which results in high assurance.
Read more about when to use data diodes and about Advenica’s data diodes and how they work!
Security Gateways
A security gateway is a device that controls the information exchange that takes place between different security domains.
If you have security sensitive or even classified information, you may need a solution that offers secure and filtered bidirectional communication. In this case, you need to ensure secure bidirectional communication and be sure that nothing malicious enters your sensitive networks, and that sensitive information and data does not leak to a less sensitive and less protected network.
The purpose is to apply strict information-level control during information transfers and mitigate cybersecurity threats such as manipulation, data leakage and intrusion. A security gateway only forwards received information when it complies with its policy which is derived from your organisation’s information security policy. The policy implemented in the security gateway defines accepted structures, formats, types, values and even digital signatures. When a message is sent from one security domain to another across a security gateway, information in the message is analysed according to the configured policy. Approved parts of the received message are put into a new message which is sent to the intended receiver in the other domain. In this way, you know that only allowed information crosses this boundary.
Advenica’s solution is ZoneGuard, read more about it here!

Digital Responsibility – more than technology
With innovative and future-proof technology solutions, you have the right tools to take your digital responsibility. However, information security entails more than technology.
People and processes are equally important to succeed. Sustainable protection requires systematic and continuous work based on assets, threats and risks.
The first step is to understand which information that is critical to business. A risk and security analysis help you identify the problems as well as specify and prioritise necessary measures. However willing you are to protect your information; it is not practical or financially justified to protect all information in the same way and the next step is to make some decisions based on the analysis.
So what does Digital Responsibility entail?
Digital Responsibility should be seen as an absolute need to ‘do good’ with your digital technology and your digitalisation efforts. This requires a balanced and conscious priorisation between three partly conflicting cornerstones:
- Digital Functionality
- Digital Privacy
- Digital Sustainability
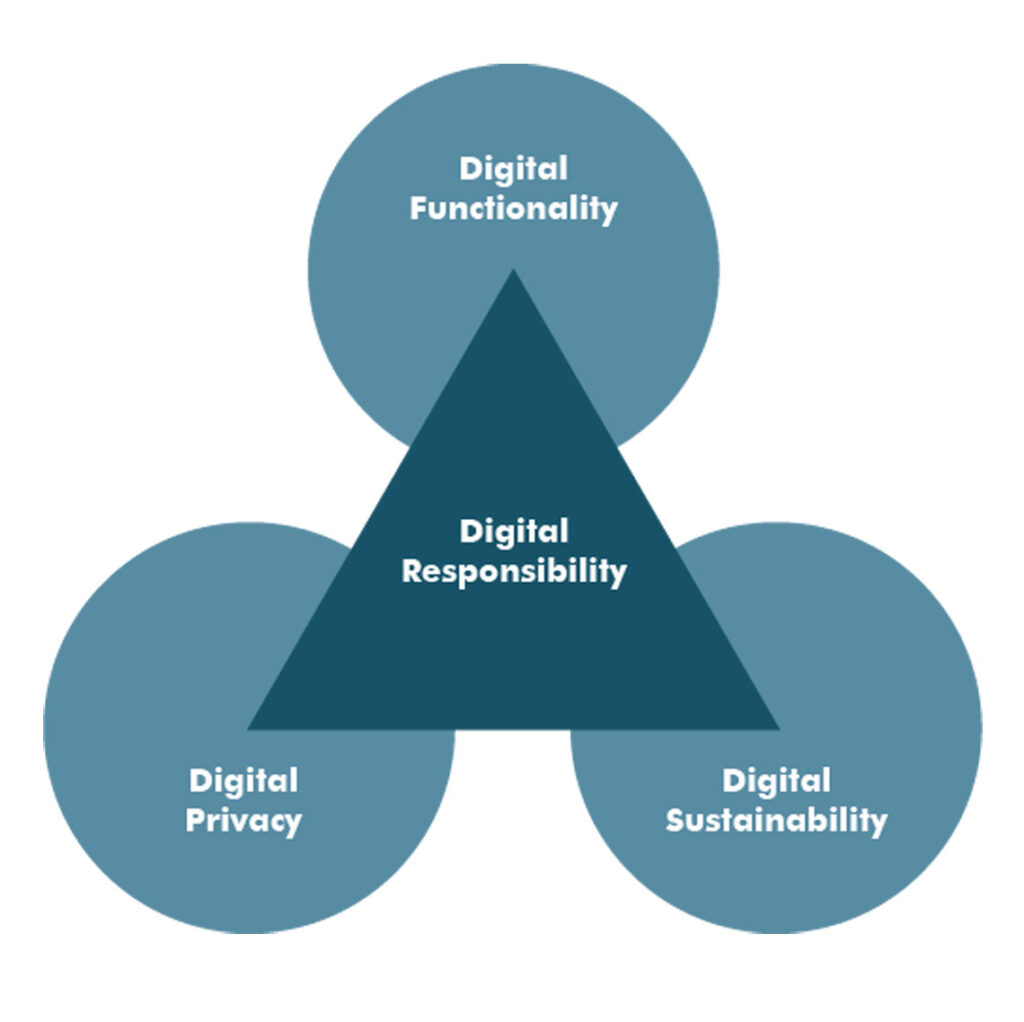
Digital Functionality
Technology advancement is inevitable. The digitalisation currently ongoing is necessary. As a society we need to extend our possibilities of measuring, collecting and processing information to be able to in a more optimised way:
- Use the limited resources we have
- Plan to minimise scrap, and…
- Find new opportunities that can either directly create values or indirectly through increased entrepreneurship and innovation.
Within functionality, you find possibilities for innovation and opportunities for new and extended business as well as the more mundane functions that ‘have always been there’. The responsible approach is not to avoid development and digitalisation or progress beyond. The responsible approach is to balance Functionality with the other two cornerstones.

Digital Privacy
The second cornerstone is the responsibility for Digital Privacy. The right to privacy is part of the universal declaration of human rights. In Europe, the awareness of issues related to privacy have made a recent jump due to the EU GDPR regulation that went into force in May 2018. Regardless of regulation, Digital Privacy must be part of any technology design ahead. Not only from a short-term point of view but also with a concern for possible long-term effects.
The traditional information security objectives: confidentiality, integrity and availability is now complemented by three new objectives: unlinkability, transparency and influence. These goals are contradictory pairs; one can not, for example have maximum availability and maximum confidentiality at the same time. Therefore, it becomes a necessity to understand the implications of different technical design decisions so that the solutions being built are balanced between the different objectives. The focus is about to shift from the traditional objectives against the new.
Digital Sustainability
The third cornerstone is Digital Sustainability. The digital functionality we build and the digital capabilities our newly technology enables should aim to follow a digital version of the Hippocratic Oath: ‘abstain from doing harm’. Our society is moving very slowly towards a kind of hypersensitivity to disruptions in our digital technology. This is apparent in technology surrounding critical infrastructure in which a lack of Digital Responsibility can have dire consequences. Attacks or even poor implementation in the IT and OT systems surrounding our core infrastructure can easily put great values or even lives at risk. There are other needs for digital sustainability. Burying waste or dumping it into the ocean was acceptable in the past because we ‘didn’t know better’. Future effects on our society due to ‘digital spill’ in terms of breaches and leaks or the huge ‘social memory’ built by social media are unknown. All of the three cornerstones above carry responsibility. At the basic level, there is a need for Digital Accountability. The functionality we include in our technology, the choices we make in our designs and the data we choose to collect will affect our common future. Worth noticing is that (digital) security is not a cornerstone in itself. IT and information security are the tools by which we will accomplish many of the responsible actions necessary.

At every decision, Digital Responsibility should force a strategic view so that a balance is established between the Digital Functionality put in place and its short and long-term effect on Digital Privacy and Digital Sustainability.
The responsibility extends to more than the current year. You need to assume responsibility for potential future uses and misuses of your collected data and your implemented functionality. If your actions today could be used in a hostile way by tomorrow’s actors, you should use a principle of caution today. If your technology can be misused tomorrow, you are responsible today.
Security culture – an important part of cybersecurity
Cybersecurity today is not only a technical challenge but also a human challenge – a matter of security culture. Criminals do not always only exploit technical deficiencies but often rely on people to access sensitive data and it is therefore the human factor that causes the most serious security breaches. Building and maintaining a strong security culture is therefore an extremely important part of cybersecurity work.
Security culture is the shared values, conceptions, attitudes, knowledge and behaviour of individuals and groups in an organization focused on creating security in the business. Safety culture is about how employees’ values affect the way they think and act in relation to risk and safety. It therefore has a great impact on how people work and influence employees on a daily basis.
In a good security culture, everyone is aware of the risks and has both the knowledge and the will to contribute to reducing the risks through their actions. Security thinking is an obvious part of the business. In other words, the security culture has a great importance on how to work, prioritize and in different ways create the conditions for employees to work securely. Another thing that characterizes a good security culture in a workplace is that management prioritizes and handles security issues at all levels of the business and that they are part of the culture.
Laws and regulations
A part of taking digital responsibility is to oblige laws and regulations that are aimed at protecting sensitive information. Digitalisation not only creates business opportunities but opens more attack vectors to systems. The number of cyberattacks has increased sharply over the recent years, not only from criminals and script kiddies but also from state-funded forces with great endurance and vast resources. Raising information security within critical infrastructure raises society’s readiness for external disturbances.
The NIS Directive
The NIS Directive tightens the requirements for information security in terms of integrity and availability. It is important to take people, processes and technology into account to ensure information security in the affected organisations. Better understanding in general of information and system risk classification together with impact contingency and action plans is necessary to improve resistance to attacks. Incidents are to be reported as part of increasing knowledge and raising preparedness. Basically, focus lies on the network and information systems that are used.
GDPR
By legislating meaningful rights for the individual, and the corresponding obligations on the organisations who manage the information, the power of the information is transferred to the individual. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) brings revolutionary changes in IT systems. It also involves major efforts to adapt all the systems and procedures to the new requirements. This opens up great opportunities for those who deliver services and products in the field of information security. It is no exaggeration to compare the scope of work with the Y2K adaptation.

How do you take your digital responsibility?
Time to start working. If you are a C-level executive, just start balancing your work of building new functionality, increasing operational efficiency and creating new business opportunities with the decisive act of Digital Responsibility. If you are not currently at C-level in your company, you can start discussing related topics around Digital Responsibility to move the subject towards the bigger question of responsibility and accountability rather than tackling every issue on its own. If you want to start working proactively with digital responsibility, for example in the digital privacy area, here are five action items:
- Involve. Start involving your management and board in discussions and reflections on your current Digital Responsibility position.
- Take stock. Identify the information you store, transport and process which thereby needs protection
- Inform. Be clear in your communication to your customers whose data you manage on how you will protect their information.
- Think privacy by design. Whoever designs without understanding these impacts will need to be correct in hindsight – something that will always be more expensive than doing it right from the start.
- Consider laws and regulations that demand that you take responsibility.
Why you should do a risk analysis
In order to know in which direction to go with your cybersecurity work, you must evaluate the business as it is today – by making an analysis of the risks that currently exist in the business’s system.
An initial, simple risk analysis identifies the worst that can happen today without having introduced any risk-reducing measures. Later, a detailed risk analysis is performed for separate zones and flows. This step is taken when the groupings of zones and flows have been made, based on the initial risk analysis.
The goal of these risk analyses is to ultimately be able to apply the right risk-reducing measures and create a more secure business where focus is put in the right places.
Read more how to do both the initial and the detailed analysis.
Why you should work with network segmentation
An important part of improving your cybersecurity is working with network segmentation. Network segmentation in data networks means dividing a data network into subnetworks, where each is a network segment. The benefits of such splitting are mainly to improve security and performance. Without segmentation, there is a risk that sensitive information can be leaked or manipulated, and that malware and ransomware can spread unchecked and quickly. Attackers do not need to go directly towards the target, for example the electricity distribution. Instead, they nestle in via weak points far out in the architecture, via email or customer service, as a way to reach the goal. State-supported attackers are also patient, prepared to work long-term, do everything in small steps and, unfortunately, are often one step ahead. The stark reality is that the company’s management and control systems can be already be attacked without being noticed, yet.
There are different kinds of network segmentation:
- Physical separation
- Airgap
- Logical separation
Read more about the best ways to use network segmentation and how to implement it!
Advenica has the cybersecurity solutions you need
What are your security challenges?
- Do you need to securely integrate IT and OT systems?
- Do you need to secure your remote access?
- Do you want to be able to transfer sensitive information from a SCADA system?
- Need to find a secure solution for traceability and logging?
- Want to avoid the security risks of updating your systems?
- Do you need secure communication with remote sites?
Read more about how our solutions can help you with these and similar challenges!
Want to read event more about our products? You will find the information here!
If you need some guidance regarding digital responsibly you are welcome to contact us!






